
- Understanding Chronic Hip Pain
- Causes of Chronic Hip Pain
- Non-Surgical Treatment Options
- Signs You Might Need Hip Replacement
- Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
- Recovery After Hip Replacement
- Improving Mobility with Physical Therapy
Chronic hip pain can be debilitating, significantly impacting daily activities and quality of life. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), approximately 3.16 million hip replacement surgeries are performed annually in the United States. This statistic highlights the prevalence and effectiveness of hip replacement as a treatment for chronic hip pain.
Understanding Chronic Hip Pain
Chronic hip pain, lasting for three months or more, can arise from various conditions. It is often linked to osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease where the cartilage cushioning the hip joint breaks down. This leads to bone rubbing against bone, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) estimates that osteoarthritis affects more than 31 million adults in the United States. It is the most common type of arthritis, and its prevalence increases with age.
 Causes of Chronic Hip Pain
Causes of Chronic Hip Pain
Several conditions can lead to chronic hip pain. Understanding the causes can help determine the appropriate treatment. Common causes include:
- Osteoarthritis: The most prevalent cause, resulting in cartilage degeneration.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that leads to joint inflammation and pain.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, which are small-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the hip, often due to overuse or injury.
- Hip Fractures: Breaks in the hip bone, often resulting from falls or high-impact injuries.
- Labral Tears: Damage to the cartilage that forms the hip socket, causing pain and instability.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Advancements in knee replacement technology have transformed patients’ surgical experience and outcomes. Here are some key innovations:
Fortunately, several non-surgical treatment options can help manage chronic hip pain. These include:
- Rest and activity modification: Limiting activities aggravating the pain allows the joint to heal.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening exercises and stretches can improve flexibility, range of motion, and joint stability. Studies have shown that physical therapy can be effective in reducing pain and improving function in patients with chronic hip pain.
- Weight management: Excess weight puts additional stress on the hip joint. Losing weight can significantly reduce pain. The NIH recommends that individuals with osteoarthritis aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can manage pain, while prescription medications might be necessary for severe cases. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation in patients with osteoarthritis.
- Cortisone injections: Injections directly into the joint can provide localized pain relief. While cortisone injections can be effective in providing temporary pain relief, they should not be used as a long-term solution.
- Assistive devices: Using a cane or walker can take pressure off the joint and improve mobility.
 Signs You Might Need
Signs You Might Need
Hip Replacement
If non-surgical treatments fail to provide adequate pain relief and significantly impact your daily life, hip replacement surgery might be a viable option. Here are some signs to consider:
- Persistent pain: Pain that continues despite trying various non-surgical treatments, even at rest or at night. This persistent pain can interfere with sleep, work, and daily activities.
- Limited mobility: Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, getting up from a seated position, or bending over to put on shoes or socks. These limitations can significantly impact your independence and quality of life.
- Stiffness: Joint stiffness makes it difficult to move your hip joint freely.
- Painful limp: A noticeable limp when walking due to pain. This limp can indicate underlying joint damage and may lead to further complications.
- Impact on daily activities: Inability to participate in hobbies or activities you once enjoyed due to pain, leading to frustration and isolation.
Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
Studies have shown that over 90% of patients are satisfied with their hip replacement surgery after 10 years. This high success rate is partly due to advancements in surgical techniques and implant technology. Modern hip replacement surgery offers significant benefits for patients with chronic hip pain. These include:
- Reduced pain: Significantly reduces or eliminates chronic hip pain, allowing for a return to pain-free activity.
- Improved mobility: Hip replacement surgery increases range of motion and flexibility, leading to better walking and overall mobility. Studies indicate that it can significantly improve quality of life and function.
- Enhanced quality of life: Enables you to participate in activities you may have had to give up due to pain, improving your overall well-being.
- Increased independence: Reduces reliance on assistive devices, allowing for greater independence in daily life.
- Durable implants: Modern hip implants can last 20 years or more, depending on activity level and post-surgical care.
Recovery After Hip Replacement
Recovery from hip replacement surgery varies by individual, but a structured approach can lead to successful outcomes. Key critical moments of recovery include:
- Back home same day: Patients begin walking within one hour of surgery and are typically discharged home within two hours after the procedure.
- Pain management: Pain will be managed with medications to ensure comfort during recovery.
- Activity modifications: Avoid high-impact activities initially, but gradually increase activity levels as the healthcare provider advises.
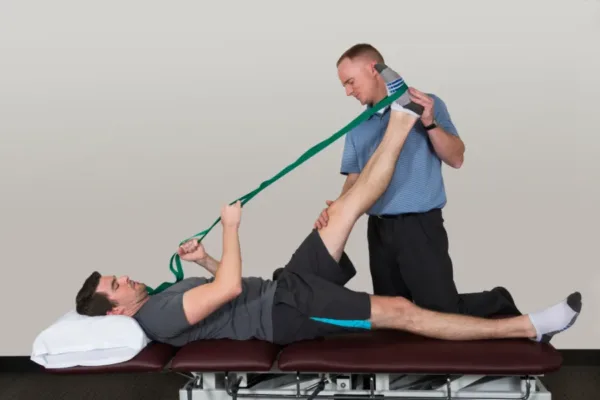 Improving Mobility with Physical Therapy
Improving Mobility with Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovering from hip replacement surgery. It can help improve mobility and regain strength. Key aspects include:
- Strengthening exercises: Focus on muscles that support the hip joint, enhancing stability and reducing the risk of injury.
- Flexibility exercises: Stretching can improve the range of motion, making daily activities easier.
- Gait training: Learning to walk properly after surgery aids in recovery and can prevent complications.
- Balance training: Helps improve stability, reducing the risk of falls as you regain mobility.
Chronic hip pain can be frustrating and limit your mobility. While non-surgical treatments can often help, hip replacement surgery offers a long-term solution for those with severe, persistent pain. We can diagnose your hip pain and discuss the best treatment options, including hip replacement surgery. If you are experiencing chronic hip pain that impacts your daily life, consult with Dr. Clegg and his staff to explore your treatment options and regain an active, pain-free lifestyle.
